Deploy and Interact with Rootstock using the MCP Server
Rootstock MCP Server is a Model Context Protocol (MCP) server that provides advanced tools for interacting with the Rootstock blockchain. This project enables AI clients to seamlessly connect and execute blockchain operations.
In this tutorial, you will learn how to interact with AI clients to automate, build and deploy innovative AI-enabled dApps on Rootstock.
Not sure about what MCPs are or how they work? Read the guide to MCPs on Rootstock.
Who is it for?
- For non developers: You can now interact with Rootstock directly from an AI client — no coding required.
- For developers: Seamlessly integrate Rootstock into Cursor or Claude to speed up your workflow, get smart assistance, and simplify on-chain development tasks.
Prerequisites
- Node.js v18 or higher.
npmoryarn- TypeScript (included in dev dependencies)
> See how to install Node and NPM.
Supported Networks
The Rootstock MCP Server is supported on Mainnet and Testnet.
- Mainnet
- Testnet
- RPC URL:
https://public-node.rsk.co - Chain ID: 30
- Explorer: https://explorer.rootstock.io
- RPC URL:
https://public-node.testnet.rsk.co - Chain ID: 31
- Explorer: https://explorer.testnet.rsk.co
Project Structure
- ▾📂src
- ▾📂handlers
- responsesHandler.ts
- ▾📂tools
- ▾📂constants.ts
- handlers.ts
- schemas.ts
- types.ts
- ▾📂constants.ts
- ▾📂utils
- responses.ts
- index.ts
- server-config.ts
- types.d.ts
- ▾📂handlers
- 📂build
- package.json
- tsconfig.json
- README.md
Installation and Build
Clone the Repository
git clone https://github.com/rsksmart/rsk-mcp-server
cd rsk-mcp-server
> See the NPM Package
Install Dependencies
npm install
Build the Project
npm run build
This command:
- Compiles TypeScript to JavaScript in the
build/folder - Makes the main file executable (
build/index.js)
Verify Installation
node build/index.js
You should see the following response:
# node build/index.js
DevX MCP Server running on stdio
Important Note: For local running this MCP, your client will point to the
index.jsfile created on thebuildfolder after building it.
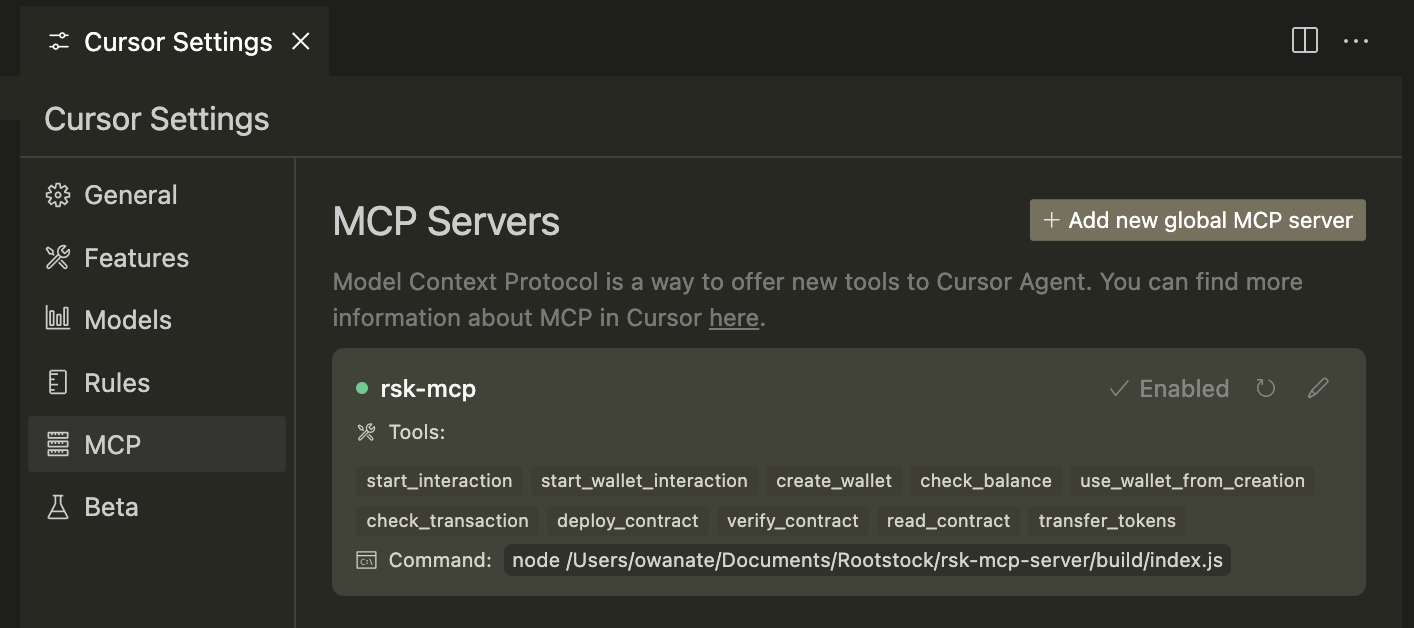
Configuring the MCP Server
There are two ways to configure the MCP Server:
- Local Configuration using AI clients such as Claude or Cursor
- Remote Configuration using publicly available endpoint
Note: You will use this Model Context Protocol Server from a LLM Client (e.g Cursor, Claude, Warp, etc) which needs to be compatible with the MCP standard.
For detailed set up instructions, please refer to the MCP Server README AI Client configuration guide.
For remote configurations with AI clients like cursor and claude, connect using the NPM Package.
Interact with MCP
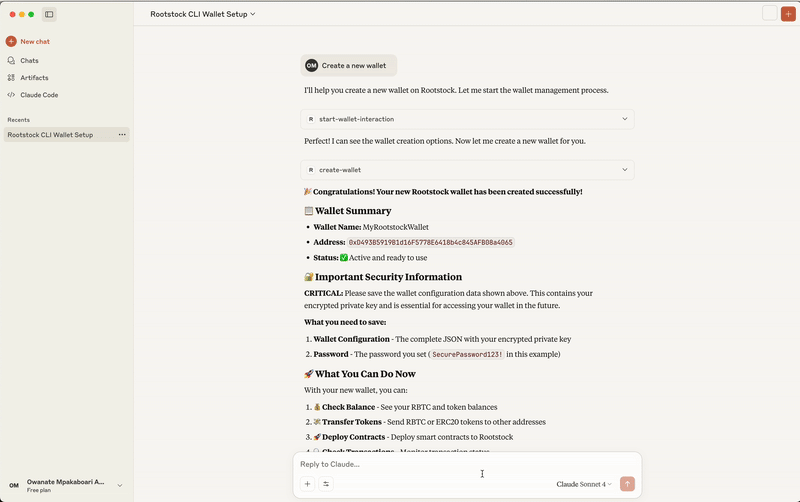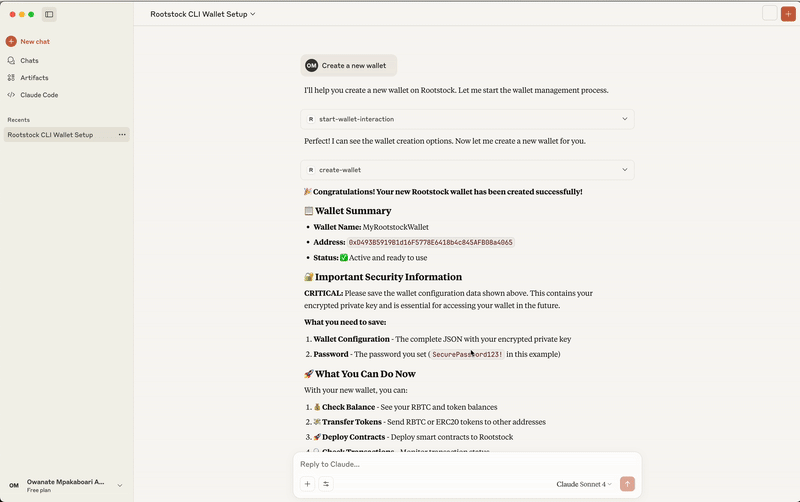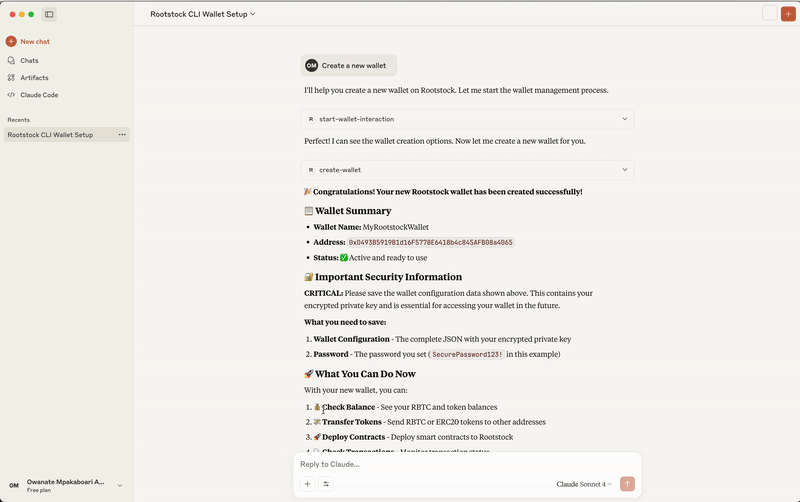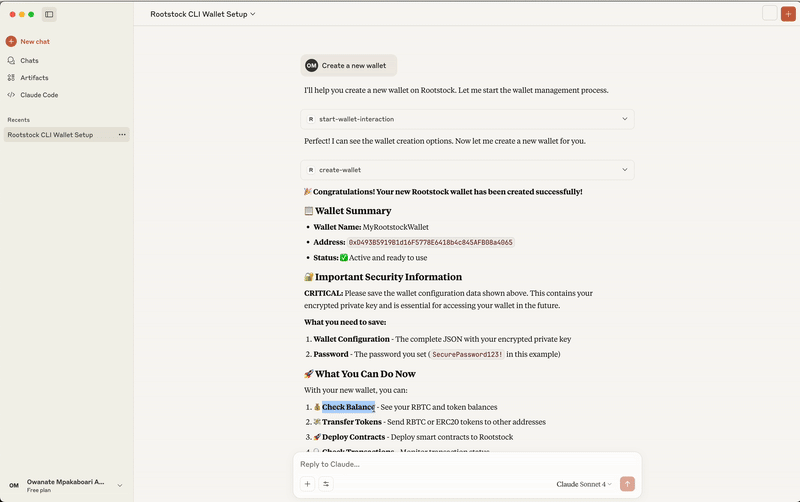
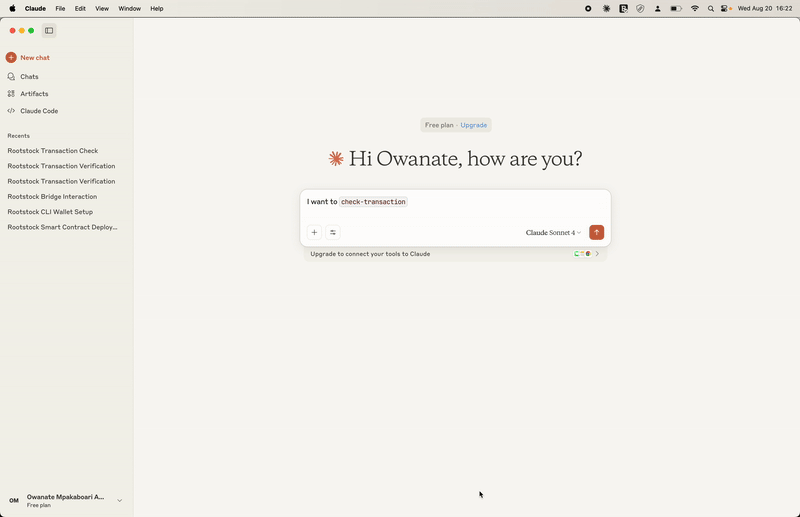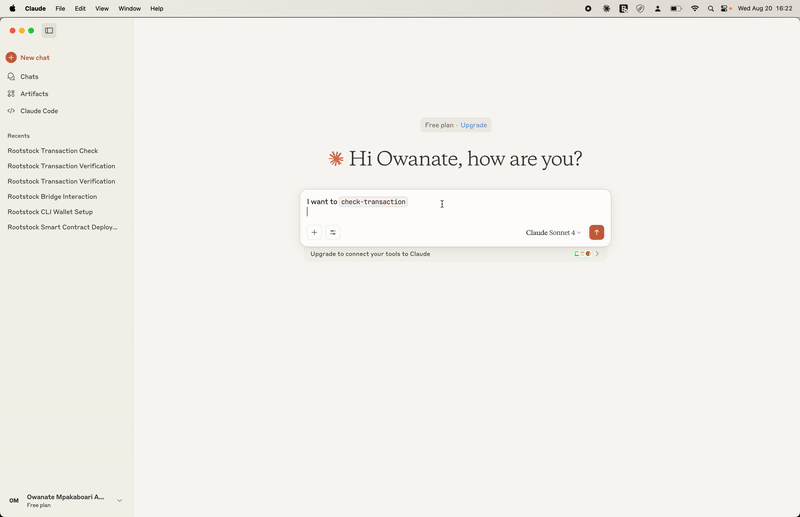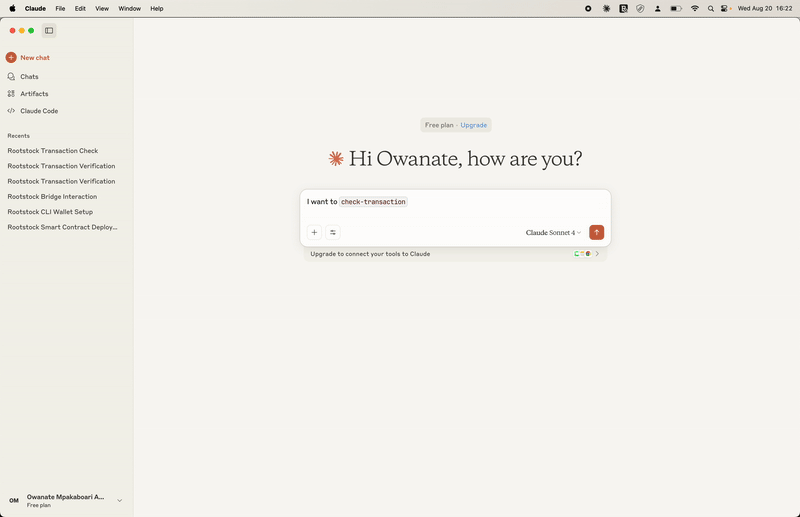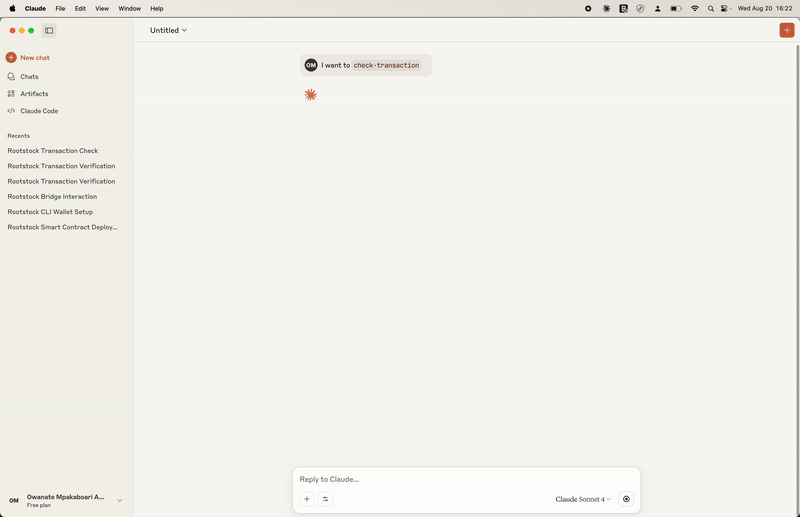
Prompt: I want to interact with Rootstock
> This requests permission to use the MCP tool, you click on Allow Once or Always Allow:
AI Response:
- “Great! Now you have access to all the Rootstock CLI functions. Here are the available options:”
Next Step:
- Create a new wallet - Generate a fresh wallet with new private keys
Deploying a Contract with the MCP
To perform complex operations like Contract Deployment. You will prompt the AI to do the following:
- Prepare Contract Files
- Compile and Deploy Your Contract on Remix
- Fetch the ABI and Bytecode
Prompt: I want to deploy a contract on Rootstock Testnet
AI Response: “Excellent! I'll help you deploy a smart contract to the Rootstock blockchain using your imported TestWallet.”
Next Step:
To deploy a contract, I need the following information:
Required Information:
**Network Selection:**
* **Testnet** (recommended for testing) \- Free transactions
* **Mainnet** \- Real transactions with costs
**Contract ABI:**
* The JSON ABI (Application Binary Interface) of your contract
* This defines the contract's functions and structure
**Contract Bytecode:**
* The compiled bytecode of your contract (hexadecimal)
* This is the actual contract code that gets deployed
**Constructor Arguments (Optional):**
* If your contract constructor requires parameters
MCP Operations
This section explains the core functions of the MCP server and how to use or integrate into your application.
Wallet Management:
This section shows you how to manage your wallets, including creating new ones, importing existing ones, and switching between them. Your wallet holds your crypto assets and is needed to sign transactions on the blockchain.
Create a New Wallet: You can create a new wallet by giving it a name and a secure password. This will generate a new address for you to use on Rootstock.
Reference:validateCreateWallet(params), processWalletOperation(params)
// In WalletService.ts
// Example parameters for creating a new wallet
{
walletOption: "🆕 Create a new wallet",
walletName: "MyNewWallet",
walletPassword: "secure_password",
replaceCurrentWallet: false
}
Import an Existing Wallet: If you already have a wallet, you can import it using its private key. You'll also need to set a new password to keep it secure on the server.
Reference:
validateImportWallet(params)processWalletOperation(params)
// In WalletService.ts
// Example parameters for importing a wallet
{
walletOption: "🔑 Import existing wallet",
walletName: "ImportedWallet",
privateKey: "0x...",
walletPassword: "secure_password"
}
List Saved Wallets: This shows a list of all the wallets you've previously saved on the server.
Reference:
validateListWallets(params)processWalletOperation(params)
// In WalletService.ts
// Example parameters for listing wallets
{
walletOption: "🔍 List saved wallets",
walletData: "my-wallets.json_content"
}
Switch Wallets: If you have multiple wallets, you can use this function to change which one is currently active for your next operation.
Reference:
validateSwitchWallet(params)processWalletOperation(params)
// In WalletService.ts
// Example parameters for switching wallets
{
walletOption: "🔁 Switch wallet",
newMainWallet: "WalletName",
walletData: "my-wallets.json_content"
}
Balance Queries:
This function checks the balance of a specific token in your wallet. It is handled within the WalletService.ts file using the balanceCommand.
Reference: checkBalanceFromCreation(params)
// In WalletService.ts
// Example parameters for checking rBTC balance
{
testnet: true,
token: "rBTC",
walletCreationResult: "..." // JSON result from a wallet creation
}
// Example parameters for a custom token balance
{
testnet: true,
token: "Custom Token",
customTokenAddress: "0x...", // contract address of the token
walletCreationResult: "..."
}
Supported Tokens: You can check the balance for rBTC (Rootstock's native token) and other popular ERC20 tokens like USDT, DOC, and RIF. You can also check the balance of any other ERC20 token by providing its contract address.
How to check a balance: Simply tell the AI which token you want to check and for which wallet. For example, you can ask for the rBTC balance in your wallet named MyWallet.
Custom Tokens: For a token that isn't on the standard list, you'll need to provide its unique contract address on the blockchain.
Transaction Tracking:
This tool lets you check the status of a transaction on the Rootstock blockchain. To use it, you need the unique transaction hash (also called a TXID).
How it works: You provide the transaction hash, and the server checks the blockchain to give you information like:
- Whether the transaction is
pending,confirmed, orfailed. - The block number where the transaction was included.
- Details about the transfer.
- The exact time of the transaction.
Contract Deployment:
This function allows you to deploy a smart contract on the Rootstock network. A smart contract is a self-executing program that runs on the blockchain.
Requirements: To deploy a contract, you'll need three main things:
- The ABI (Application Binary Interface): A file that explains the contract's functions in a human-readable format.
- The Bytecode: The compiled, machine-readable version of your contract's code.
- Your Wallet: The wallet you use for deployment must have enough rBTC to cover the transaction fees.
Process: You provide the ABI and bytecode, along with any arguments the contract's constructor needs, and the server handles sending it to the network.
Reference:
processContractDeployment(params)executeDeployment(...)
// In ContractDeploymentService.ts
// Example parameters for deploying a contract
{
testnet: true,
abiContent: `[{"inputs":[],"name":"myFunction"...}]`, // The contract's ABI
bytecodeContent: "0x...", // The contract's compiled bytecode
constructorArgs: ["arg1", "arg2"], // Optional constructor arguments
walletData: "my-wallets.json_content",
walletPassword: "wallet_password"
}
Contract Verification:
Verifying a contract makes its code public and visible to everyone. This builds trust by proving that the code you deployed matches the original source code. The core logic is in the ContractVerificationService.ts file.
Requirements: To verify a contract, you'll need:
- The contract address where it was deployed.
- The original Solidity source code.
- The compilation metadata (a JSON file that describes how your code was compiled).
- The constructor arguments used when you first deployed the contract.
Outcome: After verification, anyone can view the contract's code on a blockchain explorer and confirm it's correct.
Reference:
processContractVerification(params)executeVerification(...)
// In ContractVerificationService.ts
// Example parameters for verifying a contract
{
testnet: true,
contractAddress: "0x...",
contractName: "MyContract",
jsonContent: `{"language":"Solidity","sources":{...}}`, // Compilation metadata
constructorArgs: ["arg1", "arg2"] // Arguments used during deployment
}
Read Contracts
This tool lets you interact with smart contracts that have already been deployed and verified. You can use it to get information from the contract without sending a transaction.
- List Functions: You can start by asking the AI to list all the available functions within a verified contract.
- Call a Function: You can then call a specific function, providing any required arguments. For example, you could call the balanceOf function to check the token balance of a specific address within that contract.
Reference:
processContractRead(params)executeContractRead(...)
// In ContractReadService.ts
// Example parameters for calling a function on a contract
{
testnet: true,
contractAddress: "0x...",
functionName: "balanceOf", // The name of a 'view' or 'pure' function
functionArgs: ["0x..."] // Arguments for the function
}
See detailed functionality and supported operations in the README or the Rootstock CLI documentation.
Troubleshooting
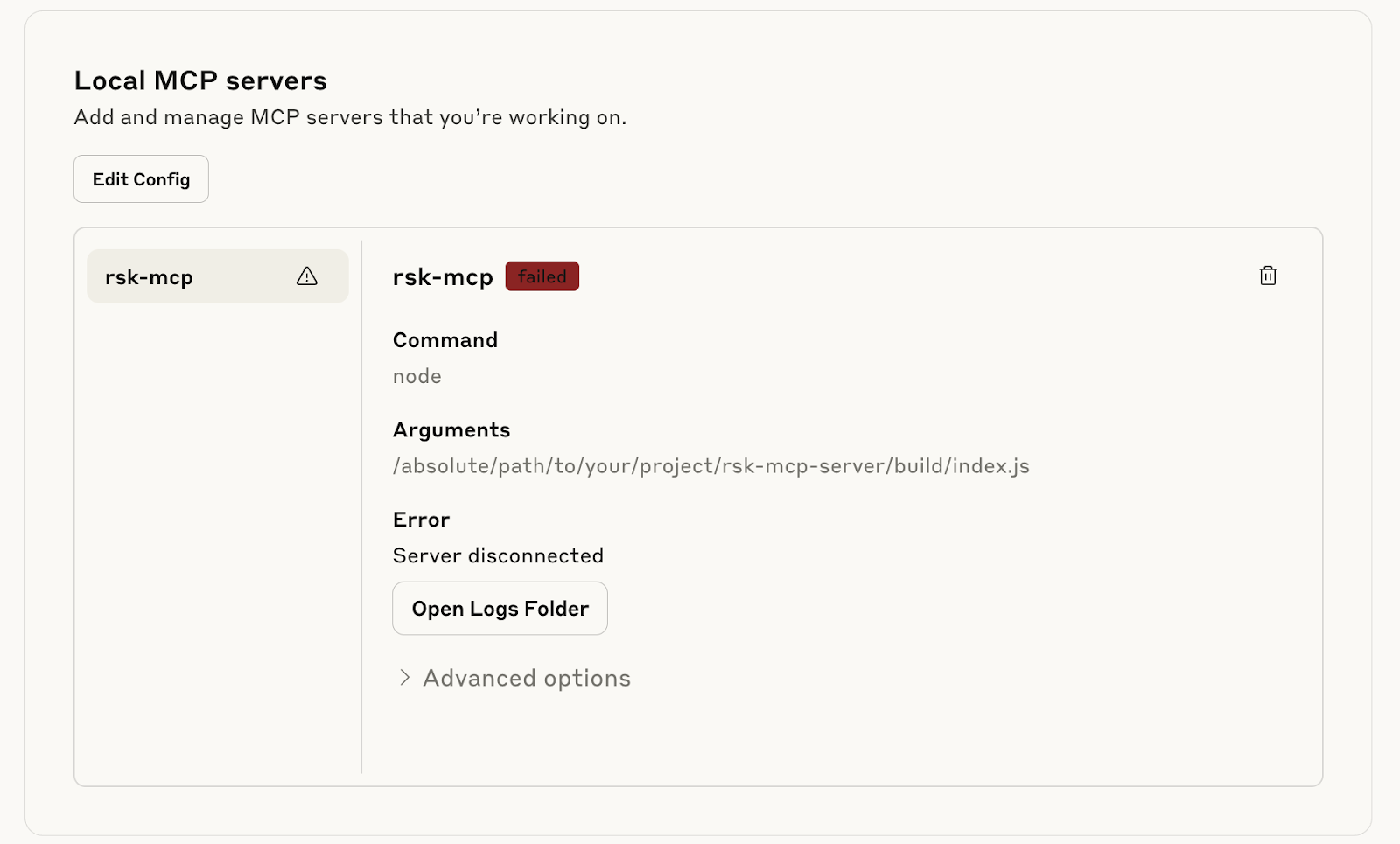
Error: rsk-mcp-server disconnected
> Ensure to edit and replace Arguments in .json text file with the correct absolute path to the index.js file, delete the current config pointing to incorrect path and add the text file.
Verify that the MCP is running:
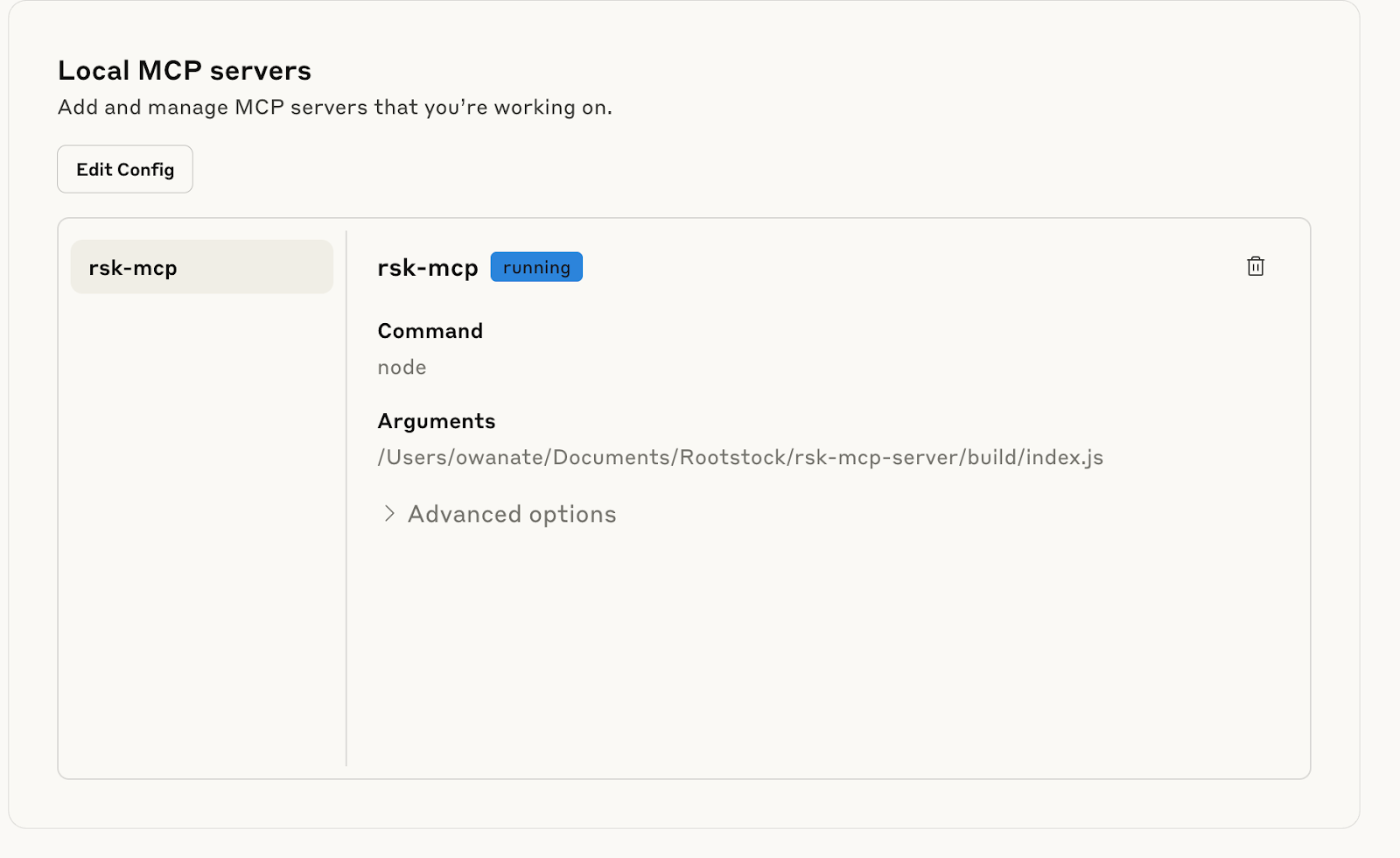
Verify that the MCP is enabled: