Best Practices for Smart Contract Development on Rootstock
Smart contracts are self-executing programs that run on blockchain networks, automatically enforcing the terms and conditions of an agreement without the need for intermediaries. On Rootstock, smart contracts play a crucial role in building decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and other trustless services. These contracts bring transparency and efficiency but also introduce unique security and good practices challenges.
Since smart contracts operate autonomously and are immutable once deployed, they are particularly susceptible to attacks if not properly designed. Vulnerabilities such as reentrancy attacks, integer overflows, and poorly validated inputs can lead to significant financial losses and data breaches. This is why adhering to best practices is essential to ensure security, reliability, and optimal performance.
In this guide, we will explore best practices for developing secure and efficient smart contracts on Rootstock, providing actionable tips to protect both the contract and its users from common pitfalls.
Security Considerations for Rootstock Smart Contracts
Security is a critical aspect of smart contract development, particularly on Rootstock, where contracts often manage large amounts of value. Due to the immutable nature of smart contracts, any vulnerability in the code can result in irreversible consequences.
In this section, we will discuss some of the most common vulnerabilities, provide mitigation strategies, and offer practical advice for writing secure smart contracts. By following these best practices, developers can ensure their contracts are resilient and protected against potential attacks.
Common Vulnerabilities
- Reentrancy
Reentrancy occurs when a smart contract makes an external call to another contract before it completes its execution. If the external contract is able to call back into the original contract, it can repeatedly execute parts of the code that should have only been run once. This creates a vulnerability that attackers can exploit by draining funds or altering the contract’s state in unintended ways.
- Example: Here is a simple example of a contract that is susceptible to reentrancy:
// Vulnerable Contract
contract VulnerableContract {
mapping(address => uint) public balances;
// Allows users to deposit Ether into the contract
function deposit() public payable {
balances[msg.sender] += msg.value;
}
// Allows users to withdraw their Ether
function withdraw() public {
uint userBalance = balances[msg.sender];
require(userBalance > 0, "Insufficient balance");
// Vulnerable external call before updating state
(bool success, ) = msg.sender.call{value: userBalance}("");
require(success, "Failed to send Ether");
// State update occurs after external call (unsafe)
balances[msg.sender] = 0;
}
}
- Mitigation: Use a reentrancy lock, for example, Open Zeppelin’s Reentrancy Guard modifier.
- Flash loan Attacks
Flash loan attacks are a form of DeFi exploit where a hacker borrows a flash loan, an uncollateralized loan from a lending protocol, and leverages it with different tactics to manipulate the market to their advantage. These attacks can happen in seconds and often involve multiple DeFi protocols.
- Example: The following diagram represents a normal flash loan
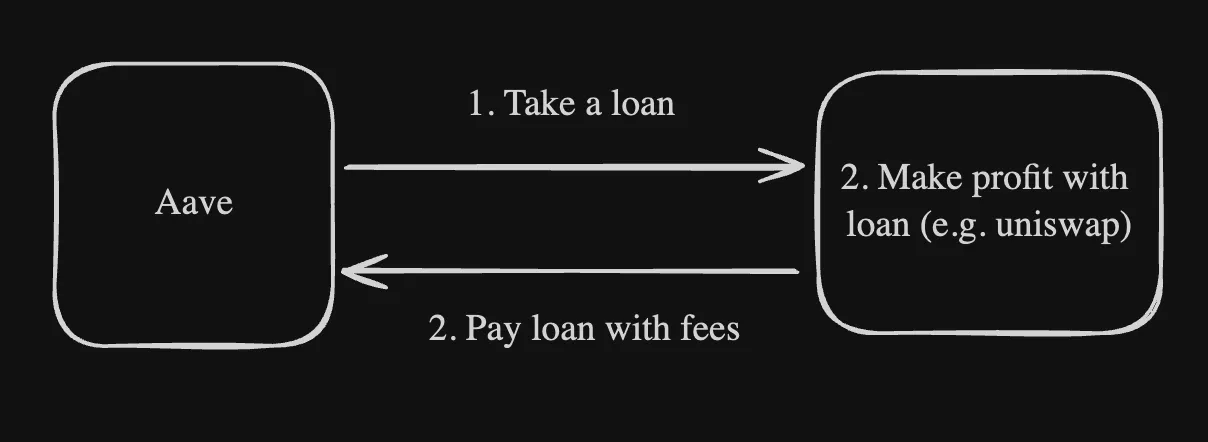
And this is an example of flash loan attack:
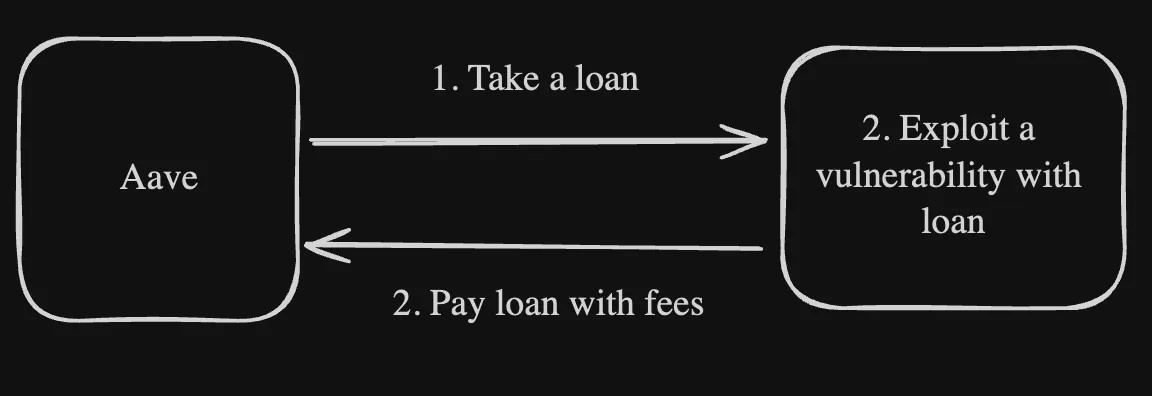
As seen above, the difference is seen in how the user uses the amount that is loaned.
- Mitigation: Even though there’s not an absolute solution for these kind of attacks, here are a few steps that can be taken to prevent these attacks:
- Use decentralized oracles for price data. See Oracles on Rootstock.
- Force Critical Transactions to Go Through at least Two Blocks
- Missing/Improper Input validation:
Missing or inadequate input validation is a vulnerability in smart contracts that arises when the contract does not properly verify or validate the data and parameters provided by users or external sources before processing. This flaw can pose serious security risks, as it may enable attackers to take advantage of the contract’s weaknesses.
- Example: This is an example of a contract missing proper input validation
contract InsecureVault {
mapping(address => uint256) public deposits;
// allows depositing on behalf of others
function addFunds(address _for) public payable {
deposits[_for] += msg.value;
}
function releaseFunds(address from, uint256 amount) public {
require(deposits[from] <= amount, "Not enough funds");
// Vulnerability: anyone can withdraw from any address due to lack of authorization check
deposits[from] -= amount;
// Incorrect variable name for 'amount' and lack of validation check can cause issues
msg.sender.call{value: amout}("");
}
}
- Mitigation: Modify the previous code:
contract SecureVault {
mapping(address => uint256) public deposits;
// allows depositing on behalf of others
function addFunds(address _for) public payable {
deposits[_for] += msg.value;
}
// properly validates the caller and the amount to withdraw
function releaseFunds(uint256 amount) public {
address payable sender = payable(msg.sender);
require(deposits[sender] >= amount, "Insufficient funds");
// Deduct the amount from the sender's balance before transferring
deposits[sender] -= amount;
// Use call with limited gas to prevent reentrancy risks
(bool success, ) = sender.call{value: amount, gas: 2300}("");
require(success, "Transfer failed");
}
}
Beyond the example provided above, to prevent this kind of vulnerability, smart contracts should enforce strong input validation, including verifying the sender’s authority, checking parameters against constraints, validating external data, and ensuring inputs stay within defined limits.
- Missing/weak access controls:
Access controls are security measures designed to limit who can access or perform actions within a system, ensuring that only authorized users can interact with critical resources or functions. While many contracts implement access controls, they are often insufficient to protect sensitive functions or data. These inadequate controls rely on simple checks, making them vulnerable to exploitation and easy to bypass.
- Example: Sample code without proper access controls
function receiveAirdrop(bytes32 calldata verificationProof[]) {
bool isVerified = MerkleProof.verifyCalldata(verificationProof, rootHash, keccak256(abi.encode(msg.sender)));
require(isVerified, "verification failed");
require(!airdropClaimed[msg.sender], "airdrop already claimed");
_transfer(msg.sender, AIRDROP_AMOUNT);
// airdropClaimed is never set to true, so the claimant can call this function multiple times.
}
- Mitigation: Clearly specify who is authorized to perform certain actions and implement these rules within the contract’s code.
function receiveAirdrop(bytes32 calldata verificationProof[]) external {
bool isVerified = MerkleProof.verifyCalldata(verificationProof, rootHash, keccak256(abi.encode(msg.sender)));
require(isVerified, "verification failed");
require(!airdropClaimed[msg.sender], "airdrop already claimed");
// Mark the airdrop as claimed
airdropClaimed[msg.sender] = true;
_transfer(msg.sender, AIRDROP_AMOUNT);
}
- Front-running attacks:
Front-running is an attack in decentralized finance (DeFi) where malicious actors exploit knowledge of pending transactions. They monitor the mempool (a list of unconfirmed transactions) and strategically submit their own transactions with higher gas fees, ensuring they are processed before the victim’s transaction. This manipulation can lead to financial losses for users and disrupt smart contract functionality.
- Example: The contract below is vulnerable to front-running due to the absence of slippage protection.
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract VulnerableSwap {
address public pancakeRouter;
address public ssToken;
constructor(address _pancakeRouter, address _ssToken) {
pancakeRouter = _pancakeRouter;
ssToken = _ssToken;
}
// Vulnerability: This function lacks slippage protection, making it susceptible to frontrunning attacks
function swapBNBForSSToken(uint256 amount) private {
address;
path[0] = IPancakeRouter02(pancakeRouter).WETH(); // First token in the swap path is BNB
path[1] = ssToken; // Second token in the swap path is SSToken
// This swap function does not include a slippage check, allowing attackers to frontrun by observing large swaps in the mempool
IPancakeRouter02(pancakeRouter).swapExactETHForTokensSupportingFeeOnTransferTokens{
value: amount
}(0, path, address(this), block.timestamp); // No slippage protection here (the '0' sets no minimum token output)
}
}
- Mitigation:
- Implement slippage restrictions: Ensure the contract checks for a minimum acceptable amount of tokens during swaps, preventing attackers from exploiting price changes.
- Use commit-reveal schemes: Introduce a two-step process where users first commit to a trade without revealing details, reducing the chances of front-running.
- Batch transactions to reduce visibility: Bundle multiple transactions into a single operation to make it harder for attackers to target specific trades.
- Monitor for front-running bots: Continuously track and detect automated bots that may be attempting to front-run transactions, enabling early intervention.
- Using libraries with vulnerabilities:
Smart contracts often rely on external libraries to implement common functionality such as token standards (e.g., ERC-20, ERC-721), math utilities, or security features like access control and reentrancy protection. However, using libraries that have undiscovered or publicly known vulnerabilities can pose a significant risk to the security of your contract. If a vulnerability exists within a library your contract depends on, attackers can exploit it to bypass security mechanisms, compromise functionality, or steal funds.
- Mitigation:
- Audit and Update Libraries Regularly: Ensure that all external libraries are thoroughly audited and are up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Use Widely Trusted Libraries: Stick to reputable, widely-used libraries (e.g., OpenZeppelin) that undergo frequent reviews and audits by the community.
- Limit External Dependencies: Avoid the excessive use of external libraries and only import code that is essential to your contract.
Considerations for Deploying to the Rootstock Mainnet
Deploying smart contracts on the Rootstock mainnet requires careful preparation and a strong focus on security. Once deployed, smart contracts become immutable, meaning that any vulnerabilities or bugs could lead to irreversible financial losses or other serious issues. Therefore, following best practices is essential to ensure a smooth and secure deployment. Below are some key considerations:
-
Audit the Contracts:
Conducting a professional audit is essential to identify potential vulnerabilities in your smart contracts. An audit helps detect issues such as reentrancy, unchecked external calls, or unsafe logic that could be exploited. This step provides assurance that your contract is secure before interacting with real assets.
-
Comprehensive Testing:
Rigorous testing is crucial. Perform unit tests, integration tests, and simulate mainnet conditions on Rootstock’s testnet. Cover all edge cases and failure scenarios, and ensure gas efficiency. This allows you to find and fix issues early, ensuring the contract operates correctly and cost-effectively in all situations.
-
Post-Deployment Monitoring:
After deployment, set up real-time monitoring to detect abnormal activity or security issues. Automated monitoring tools can alert you to potential threats, allowing for immediate action. This ongoing vigilance ensures the long-term security and performance of your smart contract.
Solidity Best Practices
Gas Optimization Techniques
Optimizing gas in Solidity is essential for lowering transaction costs and improving contract efficiency. Gas fees reflect the computational resources required, so reducing gas usage makes contracts more affordable for users and scalable for developers. Efficient contracts prevent excessive costs and reduce the risk of failed transactions.
- Storage Optimization
- Importance: Storage operations are costly. Reducing the number of storage writes and using memory instead of storage whenever possible can significantly cut gas costs.
- Example: Perform calculations in memory before updating storage variables to minimize write operations.
- Data Types and Packing
- Importance: Using optimal data types, like
bytes32over string, and packing smaller data types into single storage slots helps lower gas usage. - Example: Packing
uint8variables in a struct reduces storage costs compared to using larger types or separate slots.
- Importance: Using optimal data types, like
Fix the Solidity Pragma
When compiling and deploying your own contract, it's best to fix the Solidity version to the specific compiler you're using. This ensures consistency and avoids unexpected behavior due to future compiler changes.
Example:
pragma solidity 0.8.25;
By specifying an exact version, your contract will compile reliably with the expected behavior.
Following the Solidity Style Guide
Keep your contracts clean and organized. Here are the main highlights:
- Constructor should be the first function in the contract.
- Fallback and receive functions (if applicable) come next.
- After that, organize functions by visibility:
- External functions
- Public functions
- Internal functions
- Pure functions
- Within each group, follow this order:
- Payable functions first
- Then non-payable, non-view functions
- Finally, view functions
Use Named Imports and Specify the Library Version in the Import Statement
Instead of doing this:
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol";
Do this:
import {ERC20} from "@openzeppelin/contracts@5.0.2/token/ERC20/ERC20.sol";
By specifying the exact version of the library in your import statement, you ensure that your code remains stable even if the underlying library updates in the future. This prevents potential compilation errors or unexpected behavior due to changes in the library.
Additionally, using named imports instead of importing the entire namespace allows you to include only the specific contracts or libraries you need. This keeps your code cleaner, avoids namespace pollution, and reduces the inclusion of unused code in your compilation. While the compiler might optimize out unused code, it's best not to rely on that.
Combining both practices enhances code stability and maintainability by:
- Version Locking: Protects your code from unexpected changes in external libraries.
- Selective Importing: Keeps your codebase lean and free from unnecessary components.
Use NatSpec Properly at Both Contract and Function Levels
NatSpec (Natural Specification) comments, often referred to as "Solidity comment style," are crucial for creating human-readable inline documentation in your Solidity code. Proper use of NatSpec makes your code easier to understand for both technical and non-technical audiences, and is especially useful for documenting contracts and functions in detail.
Contract-Level NatSpec Example
At the contract level, NatSpec comments give a high-level overview of what the contract is about, its author, and its intended use. Here's an example:
/// @title Liquidity Token for the Foo Protocol
/// @author Foo Incorporated
/// @notice This token represents liquidity provided to the Foo Protocol.
/// @dev Detailed notes for developers and auditors
contract LiquidityToken {
// Contract code here
}
- @title: A short, clear description of the contract.
- @notice: A message meant for end-users or non-developers.
- @dev: Detailed notes aimed at developers to explain the technical aspects.
- @ author: The person or organization responsible for the contract.
Function-Level NatSpec Example
At the function level, NatSpec allows you to go into specifics by describing parameters, return values, and any important behavior of the function. This is especially useful for making complex logic more digestible, without relying on overly long variable names.
/// @notice Deposit ERC20 tokens into the contract.
/// @dev Emits a Deposit event upon success.
/// @dev Reverts if the token is not allowlisted or if the contract lacks ERC20 approval.
/// @param token The address of the ERC20 token to deposit.
/// @param amount The number of tokens to deposit.
/// @returns The amount of liquidity tokens received by the user.
function deposit(address token, uint256 amount) public returns (uint256) {
// Function code here
}
- @notice: A user-friendly explanation of what the function does.
- @dev: Technical details like state changes, event emissions, or failure conditions.
- @param: Describes what each function argument represents.
- @returns: Details what the function returns.
Replace Magic Numbers with Constants
When you see a number like 100 in the code, it's unclear what it represents—100 percent? 100 basis points? To avoid confusion, replace magic numbers with constants that clearly define their purpose.
Instead of this:
uint256 fee = 100;
Do this:
uint256 private constant BASIS_POINTS = 100;
Defining constants at the top of the contract improves readability and ensures that their meaning is always clear.
Use Solidity Keywords for Time and Ether Units
When working with time and ether values, Solidity provides built-in keywords to make your code more intuitive. Avoid manually calculating these values—use the appropriate keywords instead.
Instead of this:
uint256 secondsPerDay = 60 * 60 * 24;
Do this:
uint256 secondsPerDay = 1 days;
Similarly, for ether amounts:
Instead of this:
require(msg.value == 10**18 / 10, "must send 0.1 ether");
Do this:
require(msg.value == 0.1 ether, "must send 0.1 ether")
These keywords make your code more readable and easier to understand.
Use Underscores for Readability in Large Numbers
When defining large numbers, use underscores to make them more readable. This simple formatting makes it easier to understand values at a glance, especially when dealing with large denominations.
Instead of this:
uint256 private constant BASIS_POINTS_DENOMINATOR = 10000;
Do this:
uint256 private constant BASIS_POINTS_DENOMINATOR = 10_000;
Using underscores helps break up long strings of digits and improves code clarity, making it easier to spot errors and maintain the contract.
Removing the virtual Modifier from Non-Overridable Functions
The virtual keyword is used to declare a function as overridable in derived contracts. However, if you're certain that a function won't be overridden, particularly in contracts you deploy, omitting the virtual modifier can enhance code efficiency and clarity.
Instead of this:
function deposit() public virtual {
// function logic
}
Do this:
function deposit() public {
// function logic
}
Removing unnecessary virtual modifiers can improve your code and prevent potential misunderstandings.
By prioritizing security measures, optimizing gas usage, and ensuring thorough testing, you can significantly reduce the risks and enhance the performance of your decentralized applications on Rootstock.